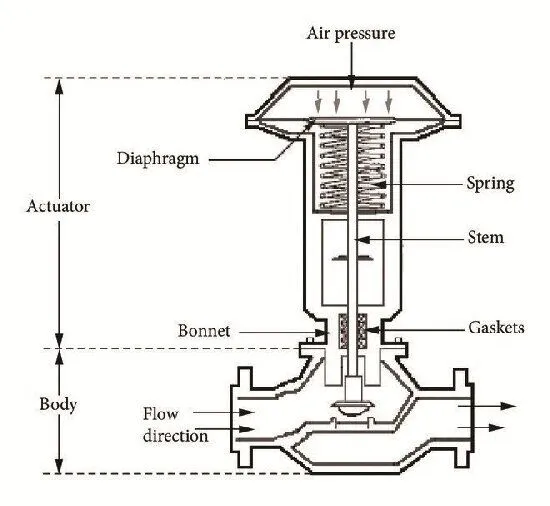
Causes and Solutions for Pneumatic Control Valve Fluctuation
On this page
As a core component of chemical production control systems, pneumatic control valves are responsible for regulating the flow, pressure, and temperature of media, crucial for maintaining process stability. However, these valves often encounter challenges with position fluctuations during operation, which not only affect control accuracy but also pose risks of equipment damage and production accidents. This article delves into the causes and solutions of pneumatic control valve fluctuation, aiming to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding and effective resolutions to this common yet critical issue.
Causes of Pneumatic Control Valve Fluctuation
Pneumatic control valve fluctuations typically result from the complex interplay of several factors, including the following aspects.
1. Control System Design Issues
Mismatched System Dynamics: Improper tuning or mismatch between the control system's dynamics (like the time constant) and the design parameters of the valve can lead to instability in valve response.
PID Controller Settings: Incorrectly set proportional, integral, and derivative (PID) parameters can cause oscillations or slow responses in the valve position, affecting its stability.
2. Performance of the Positioner
Inaccurate Calibration: Improper calibration of the positioner can result in inaccuracies in valve positioning, leading to fluctuations.
Response Time: Slow response times of the positioner can cause delayed adjustments to changes in control signals, resulting in oscillations.
3. Environmental Factors
Fluid Dynamics: Variations in fluid pressure and temperature can affect the dynamics of valve operation, potentially causing fluctuations in valve position.
Ambient Conditions: Environmental factors such as vibration or temperature changes can impact the mechanical stability of the valve and its components, contributing to fluctuations.
4. Valve Characteristics
Flow Characteristics: Inappropriate selection of valve flow characteristics relative to the application requirements can lead to difficulties in maintaining precise control, causing oscillations.
Mechanical Wear: Wear and tear on valve components over time can degrade performance, leading to increased variability in valve position.
5. Maintenance and Operational Practices
Lack of Regular Maintenance: Insufficient maintenance practices, such as infrequent calibration or lubrication, can degrade valve performance and contribute to fluctuations.
Improper Operation: Incorrect operational practices, such as abrupt changes in set points or improper handling of the valve, can induce sudden fluctuations in valve position.
Addressing pneumatic control valve fluctuation requires a systematic approach that includes proper design considerations, precise calibration of control components, attention to environmental conditions, appropriate valve selection, and diligent maintenance practices. By addressing these factors comprehensively, stability in valve operation can be achieved, ensuring reliable performance in industrial processes.
Measures for Pneumatic Control Valve Fluctuation
To effectively address pneumatic control valve fluctuation, the following technical measures and methods can be adopted.
1. Optimize Control System Design
Ensure proper matching between the control system's generalized object and locator design parameters to enhance control loop stability and response speed.
2. Fine-tune Locator Parameters
Rationally adjust PID parameters of the locator, including gain, integral time, and derivative time, to improve system stability and precision.
3. Reduce Valve Operation Friction
Optimize friction between the valve stem and packing, select appropriate sealing materials and lubrication methods to minimize operational friction losses, and reduce the likelihood of fluctuations.
4. Choosing Right Flow Characteristics and CV Values
During design and selection phases, fully consider pipeline resistance and actual flow requirements, choose suitable valve flow characteristics and CV values to avoid unnecessary adjustment difficulties and fluctuations.
5. Apply Smart Locator Technology
Utilize advanced control algorithms and adaptive functions of smart locators to more accurately address complex operational environments and control requirements, effectively mitigating the risk of valve fluctuations.
Addressing pneumatic control valve fluctuation requires systematic technical analysis and comprehensive countermeasures. By optimizing control system design, fine-tuning locator parameters, minimizing valve operation friction, selecting appropriate valve flow characteristics, and applying smart locator technology, significant improvements can be achieved in the stability and control precision of pneumatic control valves, ensuring their reliable operation and safety in chemical production.