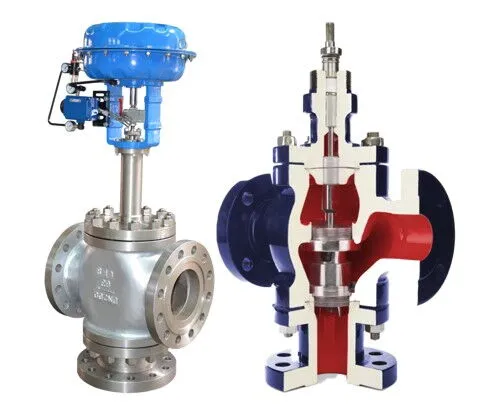
Three-Way Control Valves: Mixing Type vs. Diverting Type
Three-way control valves play an important role in industrial fluid control, especially in the mixing and distribution of fluids. Based on their operating functions, three-way control valves are primarily divided into two types: Three-Way Mixing Control Valves and Three-Way Diverting Control Valves. These two types of control valves are suitable for different control needs and are widely used across industries such as chemical, petroleum, and power generation, where they play a crucial role in precisely controlling parameters such as fluid temperature, flow, and pressure.
Three-Way Mixing Control Valve
The Three-Way Mixing Control Valve, often referred to as a mixing valve, has two inlets and one outlet. Its primary function is to mix two or more fluids together, outputting a fluid with properties that are intermediate between the input fluids. In practical applications, this valve is used for temperature control, flow mixing, and adjusting the characteristics of the medium.
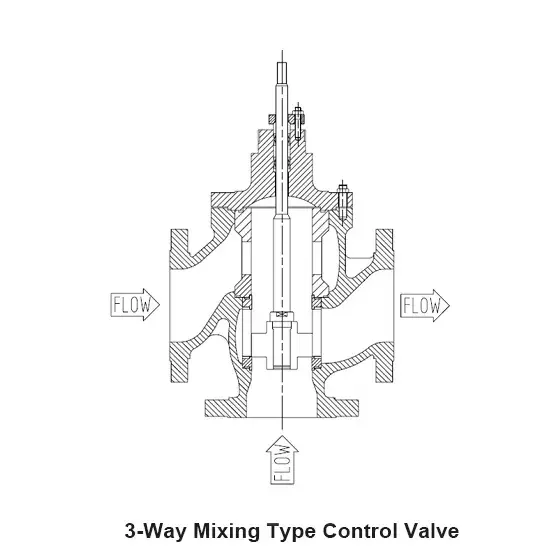
1. Working Principle of Three-Way Mixing Control Valve
When fluid flows into the valve from the two inlets, the valve plug adjusts the opening according to the set control signals, thereby regulating the mixing ratio of the two different fluids. This ultimately results in the output of the desired fluid. The change in valve opening directly affects the characteristics of the mixed fluid, such as temperature and concentration.
2. Three-Way Mixing Control Valve Design Features
The design of the Three-Way Mixing Control Valve typically includes flow balancing functionality. The movement of the valve plug ensures a reasonable mixing of the different fluids entering the valve. Its body design allows it to withstand significant pressure differences while maintaining high flow stability, making it suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
3. Applications of Three-Way Mixing Control Valve
The Three-Way Mixing Control Valve is commonly used in heat exchanger systems, where it mixes fluids of different temperatures to adjust the output temperature. It is also widely applied in cooling and heating processes, where it ensures precise control to maintain fluid temperature within an ideal range.
Three-Way Diverting Control Valve
The Three-Way Diverting Control Valve has one inlet and two outlets. Its primary function is to divide the fluid into two different paths. By adjusting the valve opening based on control signals, it automatically regulates the flow distribution to meet the demands of different parts of the system. The working principle and application characteristics of the Three-Way Diverting Control Valve make it widely used in various industrial fields, especially in applications where fluid needs to be distributed to multiple paths.
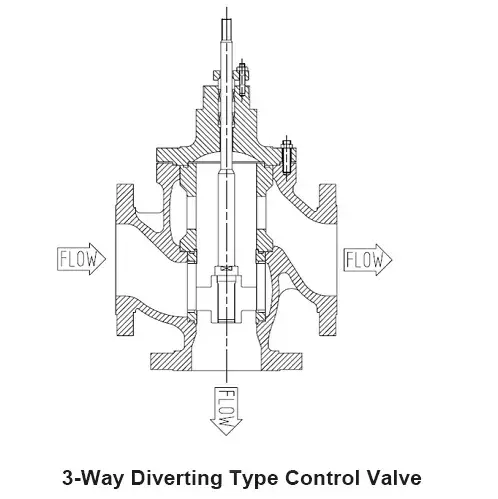
1. Working Principle of Three-Way Diverting Control Valve
The Three-Way Diverting Control Valve controls the distribution of fluid by adjusting the valve plug's opening. After the fluid enters the valve from the inlet, it is directed to the two outlets based on the adjustment of the valve plug. By adjusting the valve opening, the flow distribution ratio can be flexibly controlled to meet the needs of different diversion paths.
2. Three-Way Diverting Control Valve Design Features
The design of the Three-Way Diverting Control Valve focuses on precise flow control. The valve body is typically designed with large flow passages to ensure stable distribution even under high pressure differences. The stability of the valve plug and the smoothness of the flow paths are crucial for maintaining the accuracy of flow distribution.
3. Applications of Three-Way Diverting Control Valve
The Three-Way Diverting Control Valve is widely used in heating systems, liquid distribution, and material conveyance. In heating systems, it distributes hot water to different areas to meet the temperature requirements of each region. In liquid distribution systems, it is used to deliver fluids in specific proportions to multiple processing units.
Comparison of Three-Way Mixing & Diverting Control Valve
Although the Three-Way Mixing Control Valve and Three-Way Diverting Control Valve serve different functions, they share certain structural similarities. Both use precise valve plug control technology and can adjust the flow of fluids based on pressure changes. The primary differences lie in their working principles and application scenarios:
1. Fluid Direction and Flow Control
The Three-Way Mixing Control Valve regulates the mixing ratio of fluids, while the Three-Way Diverting Control Valve controls the distribution ratio of a single fluid. The mixing valve is used for blending and regulating multiple fluids, while the diverting valve is used to distribute a single fluid to multiple outlets.
2. Structural Design
While both types of valves share similarities in their valve body and valve plug designs, the valve plug of the Three-Way Mixing Control Valve is often ring-shaped or butterfly-shaped to ensure uniform fluid mixing. The valve plug of the Three-Way Diverting Control Valve focuses on fluid distribution and regulation. Their valve bodies also differ: the Mixing Control Valve has two inlets, while the Diverting Control Valve has two outlets.
3. Application Environments
The Three-Way Mixing Control Valve is commonly used in scenarios where fluid mixing and characteristic adjustments are needed, such as in heat exchange and cooling systems. In contrast, the Three-Way Diverting Control Valve is primarily used for fluid distribution, applied in liquid distribution and heating systems.
Three-Way Mixing & Diverting Control Valve Advantages and Challenges
Both the Three-Way Mixing Control Valve and the Three-Way Diverting Control Valve offer unique advantages, providing efficient fluid control for different needs. However, as the complexity of operating environments and technological demands increase, these valves also face certain challenges in their applications.
1. Advantages of Three-Way Mixing Control Valve
Precise Mixing Control: It enables the accurate mixing of two or more fluids, making it ideal for applications where precise control of temperature, concentration, and other fluid characteristics is necessary.
Stable Flow Characteristics: The valve provides high stability, suitable for high-pressure and large-flow control needs.
2. Advantages of Three-Way Diverting Control Valve
Efficient Flow Distribution: It can distribute a single fluid into multiple paths, ensuring precise flow control to different parts of the system.
High Flexibility: It is highly adaptable, suitable for fluid distribution, hot water supply, and a variety of other systems, meeting a range of application needs.
3. Three-Way Control Valve Challenges
Sealing and Wear Issues: In high-pressure and high-temperature environments, wear on the valve plug and seat may affect sealing performance, leading to a decrease in valve efficiency.
Control Accuracy Issues: In extreme pressure differences or high flow scenarios, the accuracy of flow control may be limited, requiring more advanced actuators and regulation systems.
Conclusion
Both the Three-Way Mixing Control Valve and the Three-Way Diverting Control Valve play vital roles in industrial fluid control. The Three-Way Mixing Control Valve ensures precise control of fluid temperature, concentration, and other properties by mixing different fluids, while the Three-Way Diverting Control Valve meets the needs of multiple fluid paths through efficient flow distribution. Whether used in heat exchangers, liquid distribution, or temperature control, these valves are indispensable in their respective applications.

